
Irregularly shaped pupils can include keyhole, ovoid, and. A prostaglandin analogue, such as travoprost, may be used if the intra-ocular pressure is elevated. Pupillary abnormalities occur in shape, size, and reactivity. To subdue inflammation, topical corticosteroids can be used. These spasms can affect any segment, or portion, of the iris and. Tadpole pupil, also known as episodic segmental iris mydriasis, is an ocular condition where the muscles of the iris begin to spasm causing the elongation, or lengthening, of parts of the iris. If the pupil can be fully dilated during the treatment of iritis, the prognosis for recovery from synechia is good. When the pupil takes on the shape of a tadpole, the condition is called tadpole pupil. Dilation of the pupil in an eye with synechia can cause the pupil to take an irregular, non-circular shape (dyscoria) as shown in the photograph. Mydriatic or cycloplegic agents, such as topical homatropine, which is similar in action to atropine, are useful in breaking and preventing the formation of posterior synechia by keeping the iris dilated and away from the crystalline lens. This blocked drainage raises the intraocular pressure. In posterior synechia, the iris adheres to the lens, blocking the flow of aqueous humor from the posterior chamber to the anterior chamber. Posterior synechia also cause glaucoma, but with a different mechanism. It is sometimes visible on careful examination but usually more easily through an ophthalmoscope or slit-lamp.Īnterior synechia causes closed angle glaucoma, which means that the iris closes the drainage way of aqueous humour which in turn raises the intraocular pressure.
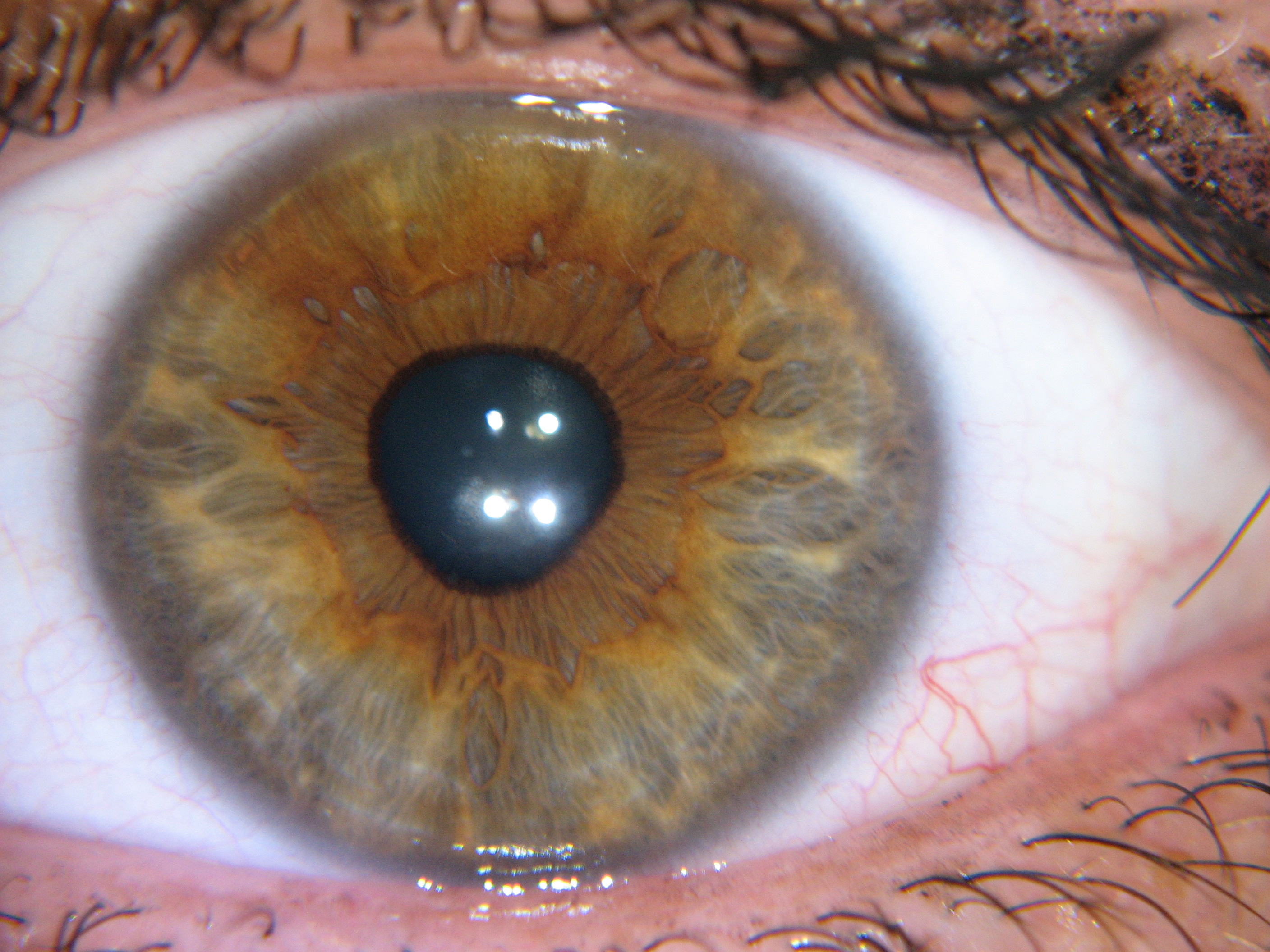
Synechiae can be caused by ocular trauma, iritis or iridocyclitis and may lead to certain types of glaucoma. Ocular synechia is an eye condition where the iris adheres to either the cornea (i.e. If the pupils are not round, this could indicate: Trauma to the eye: A scratch or other eye injury can damage the muscles in the iris, causing irregularly shaped pupils. Hence, when the muscles of the iris contract, the feline pupils take the shape of a narrow slit. Whereas the human pupil takes on a rounded, near-perfect circular shape, the cat’s pupil has an elliptical form. Misshapen pupil due to Iritis-caused synechia in the left eye One of the most striking differences between the pupils of humans and that of a cat is its shape.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
